Shoulder injuries are a common occurrence in baseball due to the repetitive throwing motions and overhead movements involved in the sport. In this post, we’ll explore the most frequent types of shoulder injuries seen in baseball players, along with how they are diagnosed, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Key Takeaways
- Baseball shoulder injuries often result from repetitive throwing motions and can cause significant pain and performance issues.
- Accurate diagnosis through physical examination and imaging is key to effective treatment and preventing long-term damage.
- Prevention strategies, such as using proper throwing mechanics, maintaining strength, and scheduling rest days, help minimize the risk of shoulder injuries in baseball players.
Common Baseball Shoulder Injuries
Shoulder injuries are prevalent among baseball players due to the sport’s repetitive overhead throwing motions. The physical stress of throwing with high velocity can place considerable stress on the shoulder joint. Over time, these repetitive motions can lead to microtraumas and an increased vulnerability to injuries.
In the following sections, we’ll explore the most common types of baseball-related shoulder injuries and their symptoms.
Labral Tears
The labrum is a ring of cartilage that helps stabilize the shoulder joint. Tears in the labrum can interfere with shoulder function by causing pain and instability. In baseball athletes, loss of throwing power is frequently reported.
Advanced imaging is typically required for the diagnosis of labral tears. Early detection and appropriate treatment can improve recovery and reduce the risk of long-term instability.
Rotator Cuff Tendinitis
Rotator cuff tendinitis refers to inflammation of the tendons in the rotator cuff, a group of muscles and tendons surrounding the shoulder that provide stability and enable a wide range of movement. Repetitive throwing, rapid increases in training intensity, and poor technique are key risk factors, as they may cause excess stress on the rotator cuff tendons, resulting in inflammation and pain after throwing.
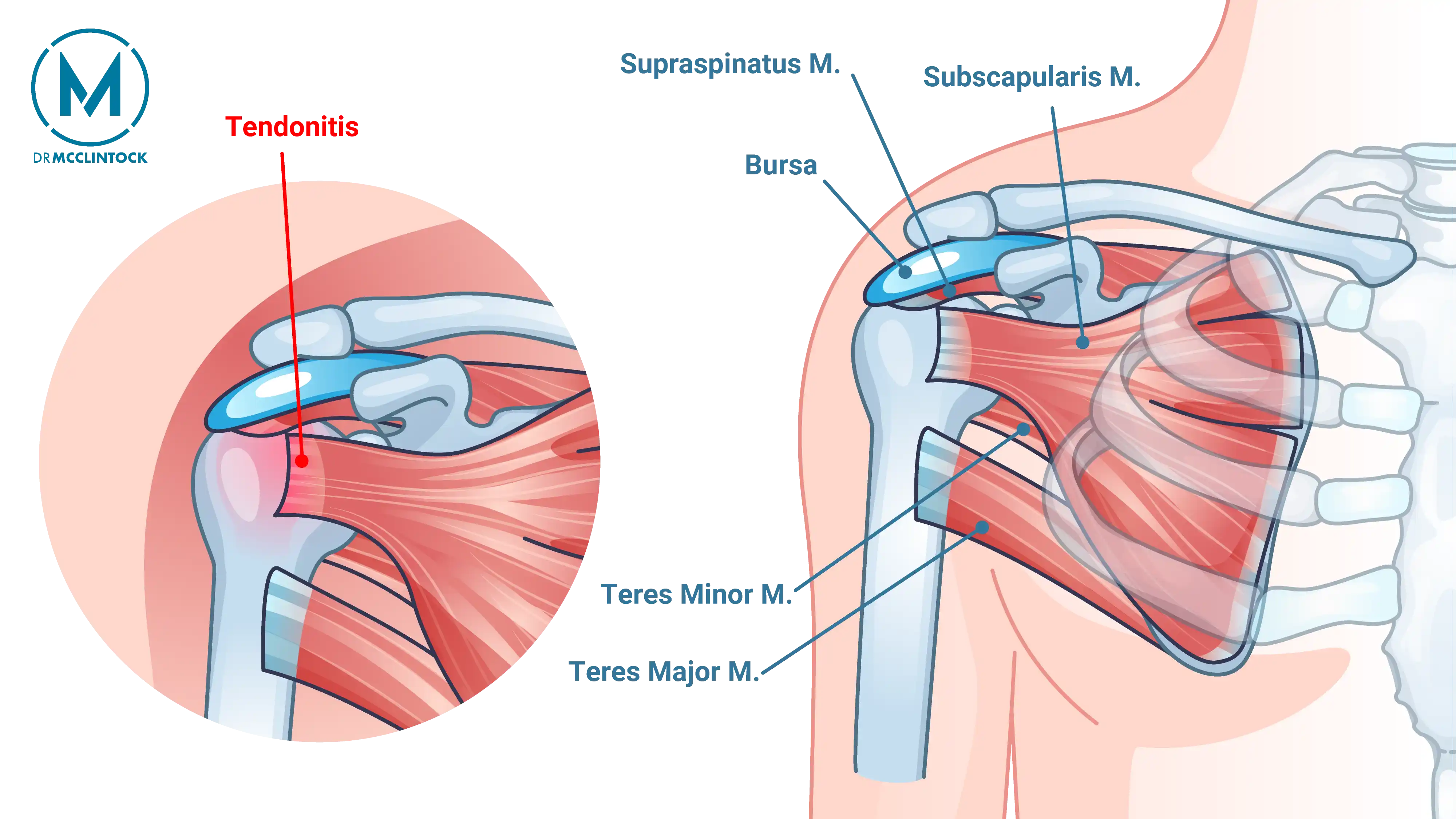
This condition can lead to significant shoulder pain, including nighttime pain that may interfere with sleep and recovery. Prompt intervention helps prevent worsening of symptoms and supports a quicker return to play.
SLAP Tears
SLAP (Superior Labrum Anterior and Posterior) tears occur when the top part of the labrum detaches from the bone. This condition typically results from the gradual wear and tear of the labrum over time, often exacerbated by repetitive throwing motions.
The symptoms of SLAP tears include instability in the shoulder joint, which can severely impact a player’s ability to throw effectively. Early diagnosis and treatment can help preserve joint integrity and function.
Shoulder Impingement
Shoulder impingement occurs when soft tissues get pinched between the humeral head and parts of the shoulder blade. Repetitive overhead movements, especially with poor form, can contribute to the development of this condition.
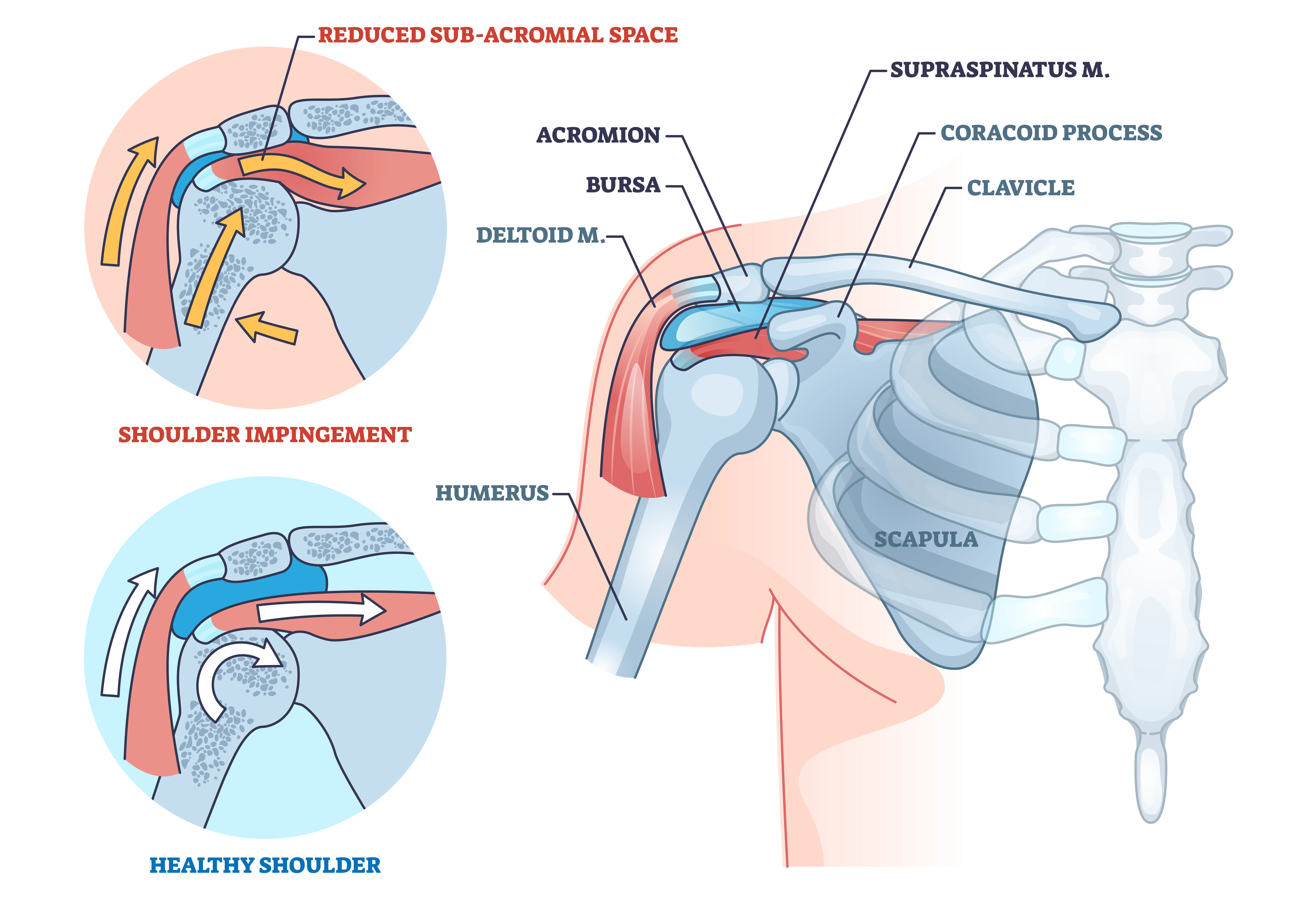
Symptoms include shoulder pain during overhead activity and diminished throwing performance. Athletes may also experience stiffness and weakness. Prevention of shoulder impingement involves understanding and utilizing smooth, controlled throwing mechanics and proper foot positioning.
Diagnosing Shoulder Injuries in Baseball Players
Accurate diagnosis of shoulder injuries enables effective treatment to prevent further complications. For many of these injuries, a combination of physical examination and imaging techniques is required.
For the physical exam, your doctor will assess the symptoms, perform range of motion tests, and evaluate muscle asymmetry and atrophy. Medical history and past injuries will also be discussed.
Imaging techniques like X-rays and MRIs are frequently used in conjunction with physical exams to provide a clearer picture of shoulder injuries. X-rays are helpful for identifying fractures and bony abnormalities, but may not detect soft tissue injuries. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide a more detailed view of soft tissues, including tendons and ligaments.
Together, these diagnostic tools help pinpoint the nature and severity of the injury, guiding the most appropriate and effective treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Injuries
Treatment options for shoulder injuries vary depending on the symptoms and type of injury. In some cases, a non-surgical approach is effective, particularly if the injury is addressed early. In others, surgery may be recommended. An experienced sports medicine shoulder specialist can evaluate the injury and work with you to determine the best treatment path for your goals.
Non-Surgical Treatments
Common non-surgical treatments for shoulder injuries include physical therapy and medications. Physical therapy generally focuses on reducing pain and strengthening the shoulder, gradually increasing in intensity over time. Medications, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), may be recommended for pain and inflammation reduction.
For some shoulder injuries, platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections may be an option. This is a medical treatment where the patient’s platelets are injected into the damaged shoulder area, promoting healing.
Surgical Interventions
Surgical intervention might be warranted for significant rotator cuff damage, labral injuries, and other shoulder conditions that do not improve with non-surgical treatment. The surgical technique used depends on the type and severity of the injury. One possible surgical intervention is arthroscopy, a minimally invasive technique involving the insertion of a small camera through tiny incisions to visualize and repair damaged tissues.
Prevention Strategies for Shoulder Injuries
Prevention strategies are essential to preserving an athlete’s shoulder health as they participate in baseball and other sports. Strength training, maintaining proper throwing mechanics, and scheduling adequate rest can help prevent shoulder injuries.
Conditioning and Strength Training
Conditioning and strength training are important for preventing shoulder injuries in baseball players. Strengthening the muscles around the shoulder can significantly enhance the stability and support of the shoulder joint, lowering the risk of injury.
If injury does occur, rehabilitation programs typically incorporate progressive strength training and sport-specific drills for a safe return to play.
Proper Throwing Mechanics
Proper throwing mechanics are key to preventing shoulder injuries in baseball. Poor mechanics, particularly during the late cocking and deceleration phases of the throw, increase strain on the joint. Correct mechanics reduce stress and prevent injuries, making it an essential aspect of training for pitchers and throwers.
Rest and Recovery
Rest days allow muscles and soft tissues to recover, helping reduce the risk of injury. Additionally, active recovery techniques, such as light stretching and low-intensity activities, can aid in healing and maintain flexibility.
Impact of Shoulder Injuries on Performance
Shoulder injuries can greatly limit performance, affecting throwing ability, pitch speed, and overall arm strength. Long-term shoulder injuries can lead to chronic pain and decreased performance, ultimately impacting how pitchers throw and a player’s longevity and career trajectory in baseball.
Short-Term Effects
Shoulder injuries can limit a player’s range of motion, impacting their ability to throw effectively. Some injuries may lead to instability in the shoulder joint, negatively affecting control and accuracy during gameplay. Sharp pain can also severely disrupt normal practice and play for an athlete.
Long-Term Consequences
Common shoulder injuries in baseball, such as rotator cuff tendinitis, SLAP tears, and shoulder impingement, can have profound long-term consequences. Persistent pain and diminished strength are concerns and can hinder a player’s career longevity and overall effectiveness in games.
These injuries can lead to a greater risk of re-injury, as the shoulder injury becomes more susceptible to damage over time. To mitigate these long-term effects and ensure a healthy athletic career, proper management and rehabilitation are necessary for those who are injured.
Managing Shoulder Injuries During the Baseball Season
Managing shoulder injuries during the baseball season requires a comprehensive approach, including:
- Monitoring activity levels and pain to make timely adjustments.
- Utilizing ice and anti-inflammatory medications to help manage pain and inflammation following shoulder injuries.
- Engaging in physical therapy, which provides targeted exercises to maintain shoulder strength and mobility while managing an injury.
A sports shoulder specialist can develop in-season injury management plans focused on maintaining performance and safety despite shoulder injuries. Open communication with coaches and medical staff about pain levels and functionality ensures informed decisions on participation, preventing further injury.
Summary
In summary, shoulder injuries are a common issue for baseball players, stemming from the repetitive, high-stress motions inherent in the sport. Understanding the various types of injuries, such as labral tears, rotator cuff tendinitis, SLAP tears, and shoulder impingement, is important for early detection and treatment. Accurate diagnosis through physical examinations and imaging techniques, coupled with appropriate treatment plans, can positively influence recovery outcomes and performance.
Prevention strategies, including conditioning, proper throwing mechanics, and adequate rest, play a key role in minimizing the risk of shoulder injuries. Physical therapy and targeted rehabilitation programs are essential for recovery, helping athletes regain their strength and mobility. By managing shoulder injuries effectively during the season and focusing on off-season recovery, players can maintain their performance. Stay informed, stay proactive, and keep your shoulders healthy to enjoy the game you love.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the most common shoulder injuries in baseball players?
The most prevalent shoulder injuries in baseball players are labral tears, rotator cuff tendinitis, SLAP tears, and shoulder impingement, typically resulting from repetitive throwing motions. Addressing these injuries early is valuable for effective recovery and prevention.
How can shoulder injuries be diagnosed accurately?
Shoulder injuries can be accurately diagnosed through a combination of physical examinations to assess muscle asymmetry and range of motion, alongside imaging techniques such as X-rays and MRIs. This comprehensive approach allows for a reliable diagnosis.
What are the best non-surgical treatments for shoulder injuries?
Non-surgical treatments for shoulder injuries include physical therapy, anti-inflammatory medications, and in some cases, PRP injections. These approaches aim to reduce pain and strengthen the shoulder joint, facilitating healing and recovery.
Why is proper throwing mechanics important in preventing shoulder injuries?
Proper throwing mechanics are essential for minimizing stress on the joint, thereby preventing injuries. Adopting correct techniques not only enhances safety but also improves overall throwing efficiency.
How important is off-season recovery for baseball players?
Off-season recovery is important for baseball players as it enables them to heal and prepare for the next season, incorporating rest and targeted exercises to improve performance and shoulder stability. Prioritizing this recovery can positively impact a player’s longevity and success on the field.





