While the most common symptom of rotator cuff tears is shoulder pain, they can also lead to numbness in the fingers. This numbness often results from nerve involvement related to the shoulder injury. In this post, we’ll explore what a rotator cuff tear is, how it sometimes causes finger numbness, and what you can do about it.
Key Takeaways
- Rotator cuff tears are shoulder injuries that can lead to significant pain, weakness, and functional limitations in the shoulder.
- Numbness and tingling in the fingers can occur alongside rotator cuff injuries, often indicating nerve-related issues that should be evaluated.
- Preventive measures, including proper exercise techniques and ergonomic adjustments, are essential to reduce the risk of rotator cuff injuries and associated symptoms.
Understanding Rotator Cuff Tears
A rotator cuff tear is an injury to the tendons of the shoulder joint. The rotator cuff is a group of four muscles and their associated tendons that stabilize the shoulder joint and allow for a wide range of motion. These muscles work together to keep the shoulder joint secure and facilitate arm movements, making them essential for activities ranging from lifting objects to playing sports.
Rotator cuff injuries may occur due to acute trauma or develop gradually through chronic wear and tear. Whether you’re experiencing shoulder pain from a past injury or new pain related to repetitive use, knowing more about the rotator cuff can help guide you toward appropriate care.
Anatomy of the Rotator Cuff
The rotator cuff is made of four main muscles: the supraspinatus, infraspinatus, teres minor, and subscapularis. These muscles are located around the shoulder blade and attach to the head of the upper arm bone through their tendons. Each muscle plays a specific role in stabilizing the shoulder joint and allowing for a wide range of arm movements, from lifting to rotating the arm.
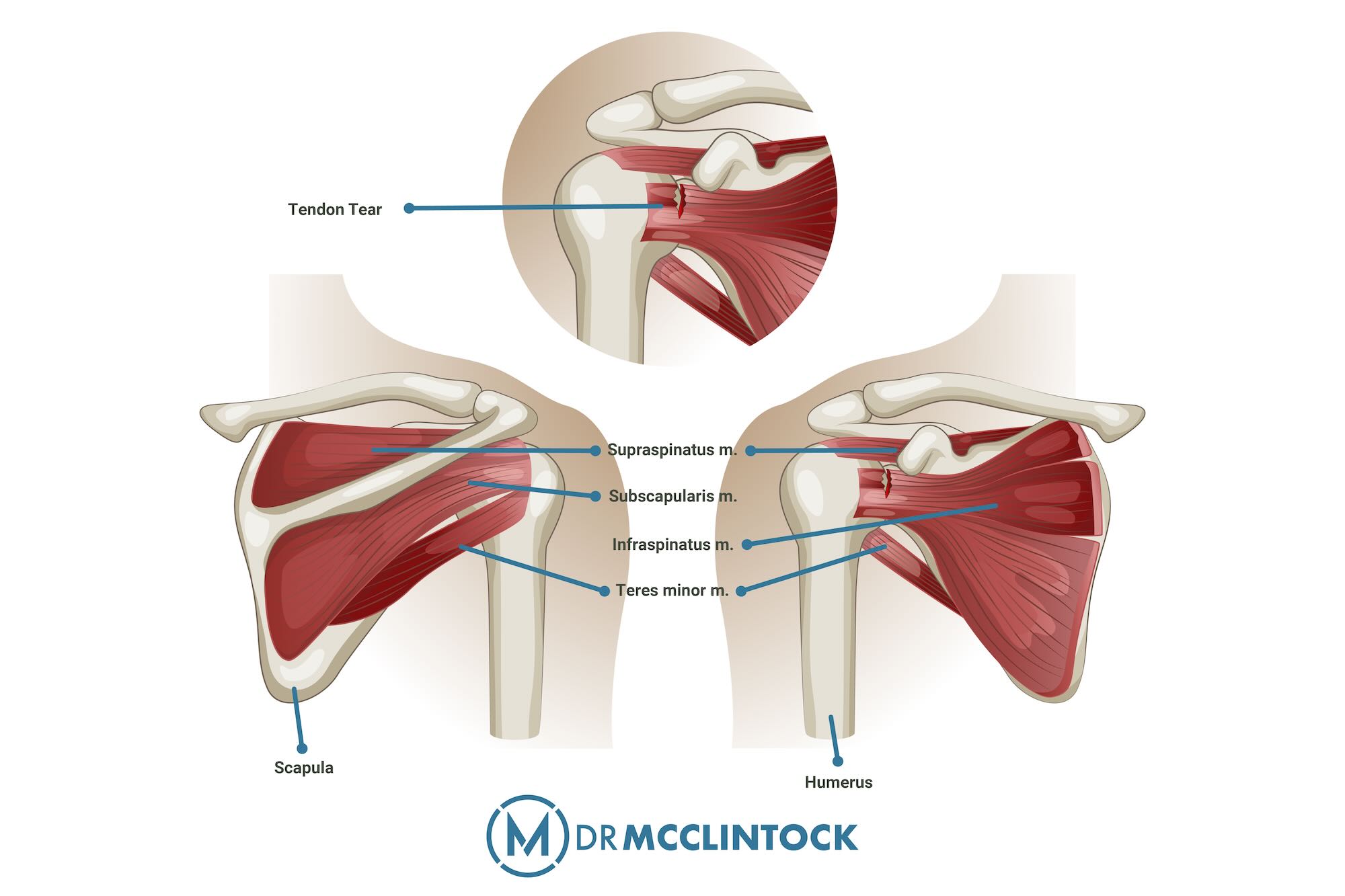
When one or more of these tendons are torn, the result is often pain, limited mobility, and a disruption to daily function. Understanding this anatomy is important to recognizing the implications of a rotator cuff tear and the importance of timely treatment.
Common Causes of Rotator Cuff Tears
Rotator cuff tears can stem from several causes, with age-related degeneration being one of the most common. As we get older, the tendons naturally weaken, making them more prone to injury. This is why rotator cuff tears are more frequently seen in older adults.
Athletes and individuals engaged in repetitive overhead activities are also at a higher risk of rotator cuff injuries. Sports such as baseball, tennis, and swimming are known for causing rotator cuff degeneration due to the repetitive overhead motions involved.
In addition to gradual degeneration, injuries can also cause tears. A sudden fall onto an outstretched hand or lifting something heavy in an awkward position may lead to a tear.
Understanding these common causes can help you take steps to prevent injury and seek care promptly if symptoms occur.
Symptoms of Rotator Cuff Injuries
Rotator cuff injuries can present with a variety of symptoms, the most common being pain. Additionally, they may cause loss of strength and functional limitations that interfere with daily activities. In some cases, numbness and tingling in the arm and hand may accompany rotator cuff injuries.
In the following sections, we’ll explore these symptoms in more detail.
Pain and Weakness
Shoulder pain is one of the hallmark symptoms of a rotator cuff injury, often described as a deep, dull ache that can interfere with sleep. The discomfort typically worsens with movements that involve lifting the arm or reaching overhead, making routine activities more difficult. Over time, this persistent pain can impact quality of life, especially if left untreated.
Loss of Range of Motion
A torn rotator cuff can significantly restrict shoulder movement due to both pain and structural damage. This limitation in the range of motion affects daily activities that require overhead reaching or lifting. For instance, simple tasks like reaching for a top-shelf item or putting on a jacket can become surprisingly difficult.
Can a Rotator Cuff Tear Cause Numbness in Fingers?
Yes, a rotator cuff injury can lead to pain, numbness, or reduced function in the hand. These symptoms can be caused by radicular pain, in which a pinched or irritated nerve root sends pain, numbness, or tingling down into the arm.
In some cases, coexisting conditions, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, can also contribute to hand numbness or tingling. Because multiple conditions can produce similar symptoms, it’s essential to determine whether the source is a rotator cuff injury or another underlying issue in order to guide appropriate treatment.
Diagnosing the Source of Numbness
Pinpointing the underlying cause of numbness requires a comprehensive diagnostic approach that includes both clinical evaluation and advanced imaging. Using these methods, your healthcare team can determine the root cause of the symptoms and advise appropriate treatment.
Clinical Examination
Diagnosing rotator cuff injuries begins with a clinical evaluation, which includes a thorough review of the patient’s medical history and a physical exam.
Motor testing is used to assess the strength of specific muscle groups in the shoulder and arm, helping to identify areas of weakness. Range of motion is evaluated through both active and passive movements to detect any limitations or stiffness that may indicate a tear. Additionally, sensory testing assesses the patient’s ability to perceive light touch and pinprick sensations in the affected arm and fingers, which may point to nerve involvement.
Imaging Techniques
Imaging techniques play a key part in diagnosing rotator cuff injuries and related nerve problems. Commonly used methods include X-ray, ultrasound, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI is particularly useful in visualizing soft tissue and nerve-related abnormalities associated with rotator cuff injuries.
These imaging techniques guide treatment planning by revealing the extent and location of the injury.
Treatment Options for Rotator Cuff Tears and Associated Symptoms
There are several treatment options for managing rotator cuff tears and their associated symptoms. These range from conservative treatments like rest and physical therapy to surgical interventions for more severe cases. Prompt and accurate treatment not only reduces pain but also can address associated symptoms such as numbness.
The severity of the tear and the patient’s overall health guide the development of a tailored treatment plan to address specific needs.
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments are often the first line of defense against rotator cuff tears. These may include:
- Rest, to allow the shoulder muscles and tendons to heal without further strain
- Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Physical therapy, focusing on restoring strength and mobility in the shoulder
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) injections, which may promote healing and reduce pain in some cases
These non-surgical options can be highly effective in managing symptoms and improving shoulder function.
Surgical Interventions
In cases where conservative treatments fail or the tear is severe, surgical intervention such as reverse shoulder replacement may be necessary.
In cases of irreparable rotator cuff tears, reverse shoulder replacement may be recommended. This procedure is designed for individuals with significant rotator cuff damage where traditional shoulder replacement would not provide adequate stability or function.
An experienced orthopedic surgeon can determine the best surgical approach based on individual needs and conditions.
Postoperative Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation after surgery is essential for optimizing shoulder recovery and function. A typical rehabilitation plan will involve a combination of stretching, strengthening, and mobility exercises to support recovery.
Working closely with a physical therapist can ensure a structured and effective rehabilitation program, helping patients regain strength and functionality in the shoulder. Sticking to the rehabilitation plan is important for achieving the best possible outcomes post-surgery.
Preventing Rotator Cuff Injuries and Nerve-Related Symptoms
Preventing rotator cuff injuries maintains shoulder function and reduces the risk of associated nerve-related symptoms, such as numbness in fingers. Making simple ergonomic adjustments and using proper exercise techniques can significantly reduce the likelihood of injury.
Ergonomic Adjustments
Ergonomic modifications can play a major role in protecting the shoulder, especially during repetitive or prolonged tasks. For example, workstation heights should be adjusted to place the elbows at a 90-degree angle to help maintain shoulder health during daily tasks like typing. If using a computer, the mouse and keyboard should be easily accessible without excessive reaching.
A specialist can provide strategies for reducing shoulder stress in occupations requiring frequent lifting. Adopting ergonomic practices in daily tasks can significantly lower the risk of shoulder injuries.
Proper Exercise Techniques
When exercising, it is important to follow proper techniques to avoid injury. To help avoid rotator cuff injuries and strengthen the rotator cuff muscles, remember to:
- Warm up with gentle stretches before exercising.
- Avoid heavy weightlifting.
- Use resistance bands for shoulder exercises to effectively strengthen muscles while minimizing strain.
To help prevent overuse injuries during shoulder workouts:
- Maintain correct posture during exercises.
- Gradually increase the intensity of shoulder exercises.
- Include breaks during long periods of repetitive shoulder activities.
- Perform stretching exercises during these breaks to reduce fatigue and injury risk.
Following these techniques helps to protect your shoulder health while maximizing the benefits of your workout.
Summary
Rotator cuff tears can lead to significant shoulder pain and functional limitations, and in some cases, may cause numbness and tingling in the fingers. Understanding the anatomy of the rotator cuff, the common causes of its injuries, and the symptoms can help in identifying the right treatment approach. Accurate diagnosis through clinical examination and imaging techniques is important for effective treatment.
There are various treatment options available, ranging from conservative approaches like rest and physical therapy to surgical interventions for severe cases. Postoperative rehabilitation and preventive measures, including ergonomic adjustments and proper exercise techniques, are essential for maintaining shoulder health and preventing future injuries. By being proactive and informed, individuals can manage and mitigate the effects of rotator cuff injuries and associated symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can a rotator cuff tear cause numbness in the fingers?
Yes, a rotator cuff tear can cause numbness or tingling in the fingers, typically due to associated nerve involvement. It’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a thorough evaluation and accurate diagnosis.
What are the common symptoms of a rotator cuff injury?
Common symptoms of a rotator cuff injury include persistent shoulder pain, arm weakness, loss of range of motion, and potentially numbness or tingling in the arm and fingers. It’s important to address these symptoms promptly to prevent further complications.
How is a rotator cuff tear diagnosed?
A rotator cuff tear is diagnosed through a comprehensive clinical examination by an orthopedic surgeon, alongside imaging techniques like X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI. This approach ensures a precise diagnosis and guides treatment planning.
What treatment options are available for rotator cuff tears?
Treatment options for rotator cuff tears include conservative methods such as rest, medications, and physical therapy, as well as surgical interventions for more severe cases. Choosing the appropriate option depends on the severity of the tear and your individual circumstances.
How can rotator cuff injuries be prevented?
To prevent rotator cuff injuries, it’s essential to use proper exercise techniques, such as warming up and incorporating resistance bands, as well as making ergonomic adjustments in daily activities to minimize shoulder strain. These strategies lower the risk of injury and support long-term joint health.





