A bicep tendon rupture is a tear of the tendon connecting the bicep muscle to the shoulder or elbow. This injury can significantly affect arm strength and function. In this post, we’ll review its causes, symptoms, and treatment options.
Key Takeaways
- Biceps tendon ruptures primarily occur in two forms: proximal (near the shoulder) and distal (near the elbow), each presenting different challenges to arm functionality.
- Common symptoms include sharp pain, a tearing sensation, a popping sound at the time of injury, bruising, and difficulty with arm movements.
- Treatment options range from nonsurgical methods like physical therapy and medications to surgical interventions, with post-operative rehabilitation playing an important role in recovery.
Understanding a Bicep Tendon Rupture
A biceps tendon rupture occurs when the tissue connecting the biceps muscle to the shoulder blade or elbow tears. Imagine the biceps muscle as the engine of your upper arm, powering movements like lifting, pulling, and flexing. When this tendon tears, it can reduce your arm strength and functionality.
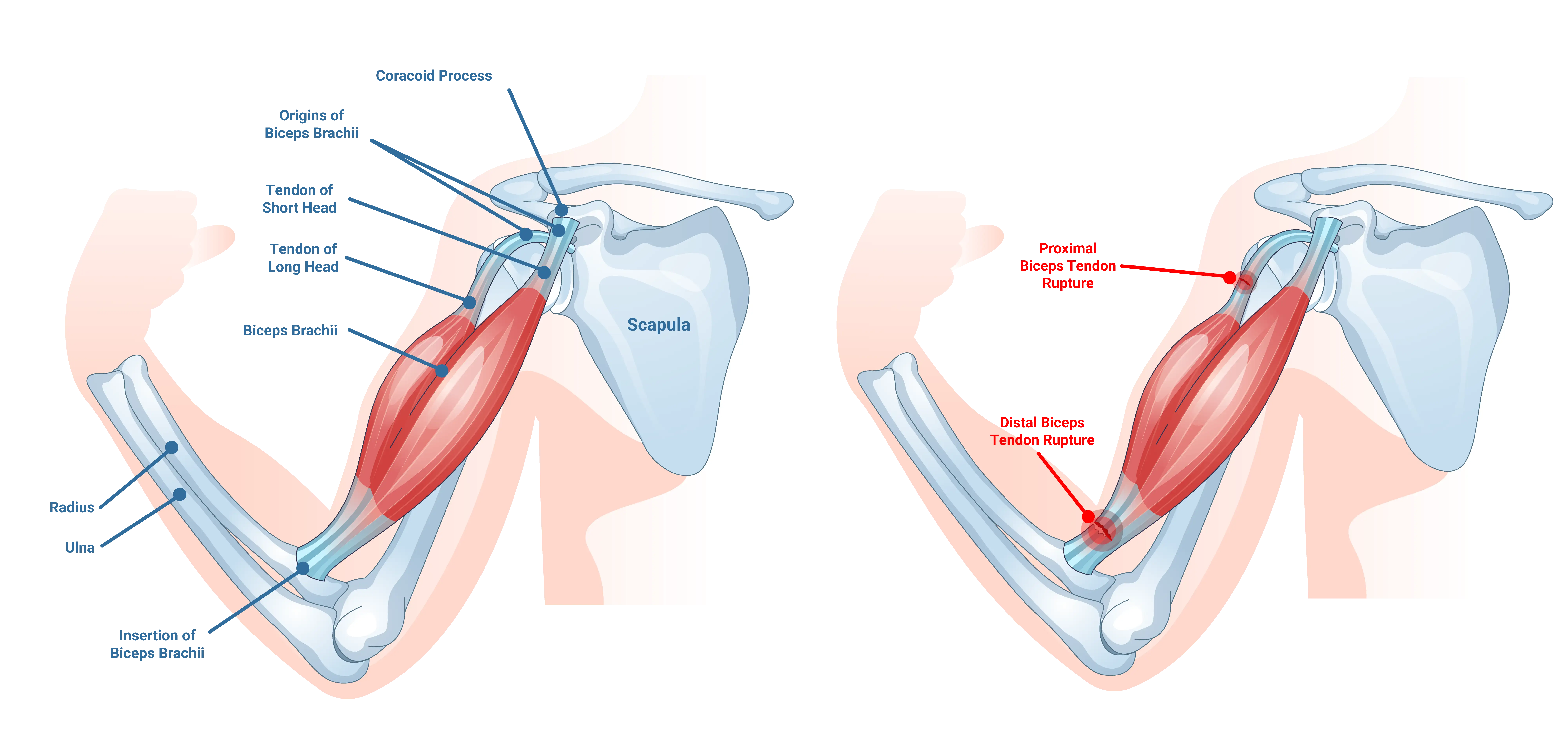
There are two main types of biceps tendon ruptures: proximal and distal. A proximal biceps tendon rupture occurs near the shoulder, while a distal biceps tendon rupture happens near the elbow. Each type has its own set of challenges and implications for arm function.
Causes of Bicep Tendon Rupture
The causes of biceps tendon ruptures can vary, but they often involve excessive force applied during arm extension. A fall onto an outstretched arm can also cause a biceps tendon rupture.
Overuse from repetitive activities may weaken the tendon, making it more susceptible to injury. Additionally, conditions like tendinosis and degenerative changes due to aging further increase the risk. A sedentary lifestyle can also weaken muscles and tendons, increasing the likelihood of injuries like biceps ruptures.
Addressing discomfort early and maintaining an active lifestyle while practicing proper techniques may reduce the risk of tendon injuries. Understanding these causes can allow you to take proactive steps to help protect your biceps tendons.
Recognizing Symptoms
Early recognition of biceps tendon rupture symptoms is important for timely intervention. One of the most telling signs is a tearing sensation accompanied by sharp pain. You might also hear a popping sound at the moment of injury.
Other symptoms may include:
- Immediate bruising
- A noticeable bulge at the elbow, often referred to as the “Popeye muscle”
- Swelling and tenderness
- A visible hollow area if the tendon retracts
- Difficulty twisting the forearm or turning the palm upward
Recognizing these symptoms early on can lead to quicker diagnosis and treatment, helping to relieve symptoms and restore function more effectively.
Diagnosing a Bicep Tendon Rupture
Diagnosis typically includes a physical examination and imaging tests. As part of the physical exam, your doctor may perform specific tests, such as the hook test and the biceps squeeze test, to assess function.
Along with the physical examination, imaging studies may be used to confirm the diagnosis and assess severity. Imaging tests may include the following:
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide detailed images of soft tissues.
- Ultrasound, which utilizes real-time, dynamic assessment to observe tendon movement.
- X-rays may be ordered to rule out fractures or other injuries.
An accurate diagnosis is important for guiding the most effective treatment plan.
Nonsurgical Treatment Options
Nonsurgical management typically focuses on reducing shoulder pain and preserving arm function. Key options may include:
- Physical therapy, focusing on exercises to help restore strength, flexibility, and shoulder stability
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) to reduce pain and inflammation
- Corticosteroid injections for short-term pain relief
- Ice therapy to control swelling
- Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy to deliver concentrated platelets directly to the injury site
For some tears, nonsurgical treatments can be effective. However, for complete tears or if these conservative treatment options fail to provide adequate relief, surgery may be recommended.
Surgical Treatment for Tendon Tears
Surgical treatment is often recommended for complete tears of the bicep tendon. Surgery often aims to reattach the tendon to the bone with the goal of restoring arm strength and function.
Various surgical techniques may be employed depending on the specifics of the rupture. These may include anchors, surgical buttons, screws, or other tools to secure the tendon. Minimally invasive arthroscopic surgery may be recommended depending on the type and severity of the tear.
Post-Surgery Recovery
Recovery after bicep tendon surgery typically spans several months, requiring a structured rehabilitation program. Rehabilitation often involves protecting the repair initially by limiting elbow flexion and rotation, followed by gradual progression of exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist.
Many patients can return to activities by around six months after surgery, though recovery times can vary. An experienced orthopedic surgeon can help guide the recovery process and provide recommendations based on the specific injury.
Prevention and Long-Term Care
Lowering the risk of biceps tendon ruptures and supporting long-term care involves several proactive measures:
- Stretching before activity
- Using slow, controlled movements while lifting weights, especially during heavy lifting
- Gradually increasing activity levels and avoiding sudden high-intensity workouts
- Maintaining proper posture and lifting technique
- Incorporating strength training
These strategies may help reduce the risk of many injuries, including biceps tendon ruptures.
Summary
Bicep tendon ruptures can significantly impact arm function and daily life. Understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnostic processes, and treatment options can help patients make informed decisions. Preventive measures and long-term care are essential for supporting tendon health. By staying proactive and informed, you can minimize the risk of severe injuries and manage them effectively if they occur.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes a bicep tendon rupture?
A biceps tendon rupture may be caused by forceful eccentric contractions, excessive force during arm extension, injuries from falls, or repetitive strain. Age-related degeneration and risk factors can also contribute.
What are the symptoms of a bicep tendon rupture?
A biceps tendon rupture typically presents with sharp pain, a popping sound during the injury, bruising, swelling, and a noticeable bulge near the elbow. Medical evaluation is often recommended if these occur.
How is a bicep tendon rupture diagnosed?
A biceps tendon rupture can be diagnosed through a thorough patient history, physical examinations, and imaging tests such as MRI or ultrasound to confirm the condition. These steps support an accurate diagnosis and guide proper treatment.
What nonsurgical treatments are available for bicep tendon ruptures?
Nonsurgical treatments may include physical therapy, NSAIDs for pain relief, corticosteroid injections, PRP therapy, and the application of ice packs. These options can promote healing and manage symptoms for some injuries.
How long does recovery take after bicep tendon surgery?
Recovery after biceps tendon surgery usually takes around six months, but exact timelines may differ based on the type and severity of the injury. Adhering to a structured rehabilitation program is often essential for restoring strength and function.